Embark on a journey into the realm of inventory management with our business inventory program. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of inventory control, optimization, and tracking, empowering businesses to streamline operations and maximize efficiency.
Dive into the depths of inventory management techniques, unraveling the nuances of FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average. Discover the strategies for optimizing inventory levels, reducing costs, and enhancing efficiency. Explore the significance of inventory tracking and reporting, gaining insights into physical counts, perpetual inventory systems, and cycle counting.
Business Inventory Program Overview
A business inventory program is a software application that helps businesses track and manage their inventory. This can include raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. A good inventory program can help businesses improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and increase profits.
Key Features and Functionalities
Key features and functionalities of a business inventory program typically include:
- Inventory tracking: The program should allow businesses to track their inventory levels in real-time. This includes the quantity of each item on hand, as well as its location.
- Purchase order management: The program should allow businesses to create and manage purchase orders. This includes the ability to track the status of orders, as well as to receive and invoice for goods.
- Sales order management: The program should allow businesses to create and manage sales orders. This includes the ability to track the status of orders, as well as to ship and invoice for goods.
- Reporting: The program should provide businesses with a variety of reports, including inventory reports, purchase order reports, and sales order reports. These reports can help businesses to track their inventory levels, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Types of Business Inventory Programs
There are a variety of different types of business inventory programs available. The best program for a particular business will depend on the size of the business, the type of inventory it manages, and the specific needs of the business.
- On-premise inventory programs: These programs are installed on the business’s own servers. They offer the most control and flexibility, but they can also be more expensive to implement and maintain.
- Cloud-based inventory programs: These programs are hosted by a third-party provider. They are typically less expensive to implement and maintain than on-premise programs, but they offer less control and flexibility.
- Mobile inventory programs: These programs are designed to be used on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. They allow businesses to track their inventory from anywhere.
Inventory Management Techniques
Inventory management techniques are essential for businesses to effectively track and manage their inventory levels. These techniques help businesses optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve customer service.
There are several different inventory management techniques that businesses can use, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common inventory management techniques include:
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
FIFO is an inventory management technique that assumes that the first items purchased are the first items sold. This means that the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest inventory items. FIFO is a simple and straightforward inventory management technique that is easy to implement.
Advantages of FIFO:
- FIFO is a simple and straightforward inventory management technique that is easy to implement.
- FIFO provides a more accurate representation of the cost of goods sold.
- FIFO can help businesses reduce their inventory holding costs.
Disadvantages of FIFO:
- FIFO can lead to higher taxes in periods of rising inflation.
- FIFO can result in stockouts if demand is not accurately forecasted.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
LIFO is an inventory management technique that assumes that the last items purchased are the first items sold. This means that the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the newest inventory items. LIFO is a more complex inventory management technique than FIFO, but it can provide some tax advantages.
Advantages of LIFO:
- LIFO can provide tax advantages in periods of rising inflation.
- LIFO can help businesses reduce their inventory holding costs.
Disadvantages of LIFO:
- LIFO is a more complex inventory management technique than FIFO.
- LIFO can lead to a mismatch between the physical inventory and the inventory records.
- LIFO can result in stockouts if demand is not accurately forecasted.
Weighted Average, Business inventory program
Weighted average is an inventory management technique that assumes that the cost of goods sold is based on the average cost of all inventory items. This means that the cost of goods sold is not affected by the order in which inventory items are purchased or sold.
Advantages of Weighted Average:
- Weighted average is a simple and straightforward inventory management technique that is easy to implement.
- Weighted average provides a more stable cost of goods sold than FIFO or LIFO.
Disadvantages of Weighted Average:
- Weighted average can be more difficult to implement than FIFO or LIFO.
- Weighted average can lead to a mismatch between the physical inventory and the inventory records.
The best inventory management technique for a particular business will depend on the specific needs of the business. Businesses should carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of each technique before selecting one.
Inventory Optimization Strategies
Inventory optimization is crucial for businesses to minimize costs, enhance efficiency, and maintain optimal stock levels. It involves implementing strategies that balance inventory levels to meet demand while reducing waste and overstocking.
A key aspect of inventory optimization is determining the appropriate safety stock levels and reorder points. Safety stock serves as a buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply disruptions, while reorder points trigger replenishment orders to avoid stockouts.
Reorder Point Calculation
Reorder point (ROP) is calculated using the following formula:
ROP = (Average Daily Demand x Lead Time) + Safety Stock
Lead time refers to the time between placing an order and receiving the inventory. Safety stock is typically expressed as a percentage of average daily demand.
Inventory Optimization Techniques
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: JIT aims to minimize inventory levels by ordering materials only when needed for production. This reduces storage costs and the risk of obsolescence.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): EOQ is the optimal quantity to order at a time to minimize total inventory costs, considering factors such as order costs, holding costs, and demand.
- Safety Stock Management: Establishing appropriate safety stock levels helps businesses mitigate the risk of stockouts while avoiding excessive inventory. Safety stock levels should be regularly reviewed and adjusted based on demand variability and lead times.
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI): VMI allows suppliers to manage a business’s inventory levels based on real-time demand data. This can improve inventory accuracy and reduce the risk of stockouts.
Inventory Tracking and Reporting

Inventory tracking and reporting are crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records of their inventory levels, monitor stock movements, and make informed decisions. It helps prevent overstocking, reduces the risk of stockouts, and ensures that businesses have the right amount of inventory to meet customer demand.
Methods for Tracking Inventory
- Physical Counts: Periodically counting the physical inventory on hand to determine the actual quantity.
- Perpetual Inventory Systems: Real-time tracking of inventory levels as transactions occur, using software or manual records.
- Cycle Counting: Regularly counting a portion of the inventory to verify accuracy and identify any discrepancies.
Inventory Reports
Business inventory programs can generate various reports to provide insights into inventory performance, including:
- Inventory Summary Report: Overview of total inventory value, quantity, and location.
- Stock Status Report: Details on the availability of specific items, including quantity on hand, on order, and backordered.
- Inventory Turnover Report: Measures the rate at which inventory is sold and replaced.
- Inventory Valuation Report: Estimates the value of inventory using different costing methods.
Inventory Control and Security
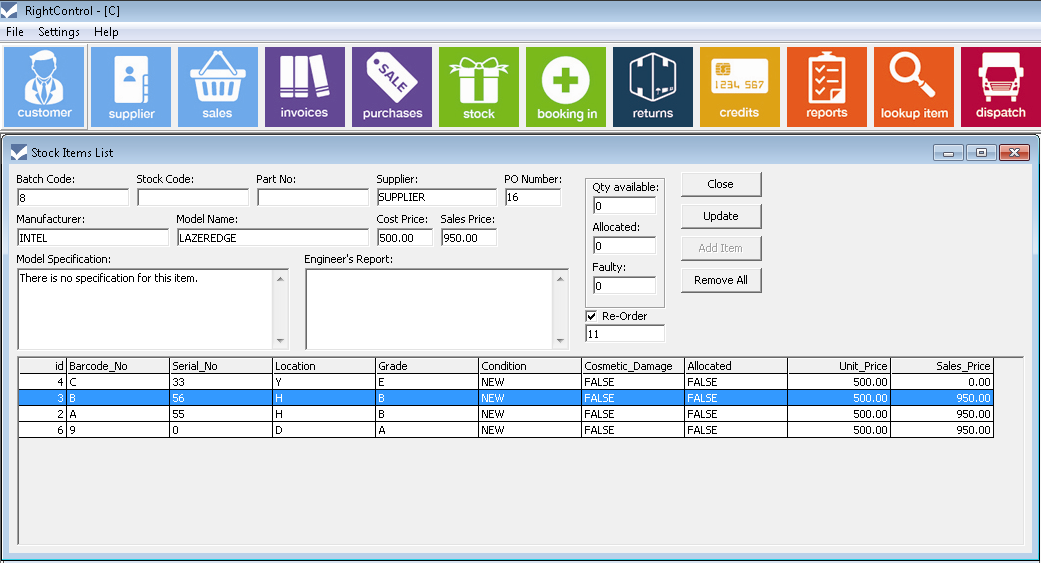
Inventory control and security measures are essential for businesses to prevent theft and loss, ensuring the accuracy and integrity of inventory records. Effective inventory control systems help businesses maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce shrinkage, and protect against unauthorized access.
Various inventory control methods exist, including:
Access Control
- Restricting physical access to inventory areas
- Implementing keycard or biometric systems
- Monitoring access logs and activity reports
Surveillance
- Installing surveillance cameras in inventory areas
- Using motion detectors and alarms
- Conducting regular physical inspections
Inventory Audits
- Performing periodic cycle counts to verify inventory accuracy
- Conducting full physical inventories at regular intervals
- Investigating discrepancies and implementing corrective actions
A business inventory program can assist businesses in implementing effective inventory control and security measures by:
- Providing real-time inventory visibility and tracking
- Automating inventory audits and discrepancy reporting
- Integrating with surveillance systems for automated alerts and notifications
- Generating reports and analytics to identify trends and areas for improvement
Integration with Other Business Systems
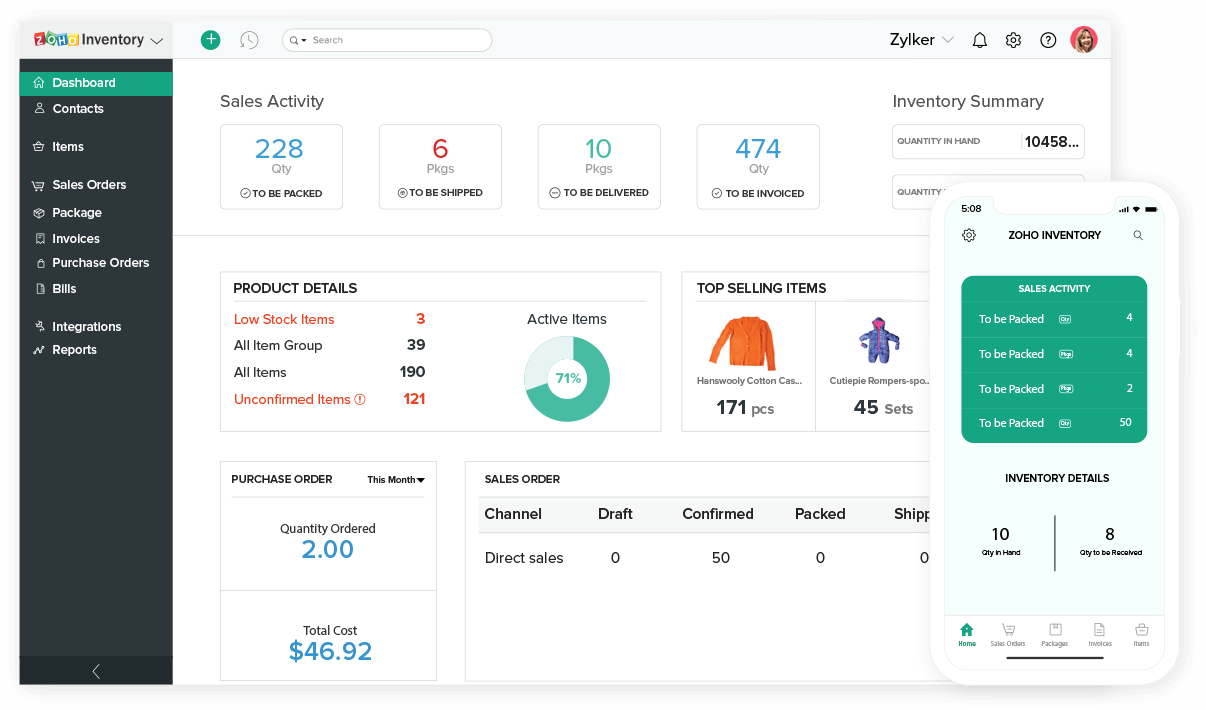
Integrating a business inventory program with other business systems, such as accounting, purchasing, and sales, offers several benefits. It streamlines operations, improves accuracy, and provides a comprehensive view of the business’s inventory.
There are different methods for integrating these systems, including direct integration, using an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, or employing middleware. Direct integration involves connecting the systems directly, while an ERP system provides a central platform that integrates all business systems. Middleware acts as a translator between different systems, allowing them to communicate and exchange data.
Integration can improve business efficiency and accuracy by automating tasks, reducing data entry errors, and providing real-time visibility into inventory levels. For example, integrating the inventory program with the accounting system can automate the creation of invoices and purchase orders, while integration with the sales system can provide up-to-date inventory information to customers and sales representatives.
Benefits of Integration
- Streamlined operations
- Improved accuracy
- Comprehensive view of inventory
- Automated tasks
- Reduced data entry errors
- Real-time visibility into inventory levels
Methods of Integration
- Direct integration
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) system
- Middleware
Examples of Integration
- Integration with accounting system: Automated creation of invoices and purchase orders
- Integration with sales system: Up-to-date inventory information for customers and sales representatives
Concluding Remarks: Business Inventory Program
In conclusion, a business inventory program serves as a cornerstone for effective inventory management, enabling businesses to gain control over their stock, optimize operations, and drive profitability. By embracing the best practices Artikeld in this guide, businesses can unlock the full potential of their inventory and achieve operational excellence.
General Inquiries
What are the benefits of using a business inventory program?
A business inventory program streamlines inventory management, reduces costs, improves efficiency, enhances accuracy, and provides valuable insights for decision-making.
How can I optimize inventory levels using a business inventory program?
Business inventory programs provide tools for setting safety stock levels, reorder points, and implementing inventory optimization strategies to minimize overstocking and stockouts.
What are the different inventory tracking methods available in a business inventory program?
Business inventory programs offer various tracking methods, including physical counts, perpetual inventory systems, and cycle counting, allowing businesses to maintain accurate and up-to-date inventory records.